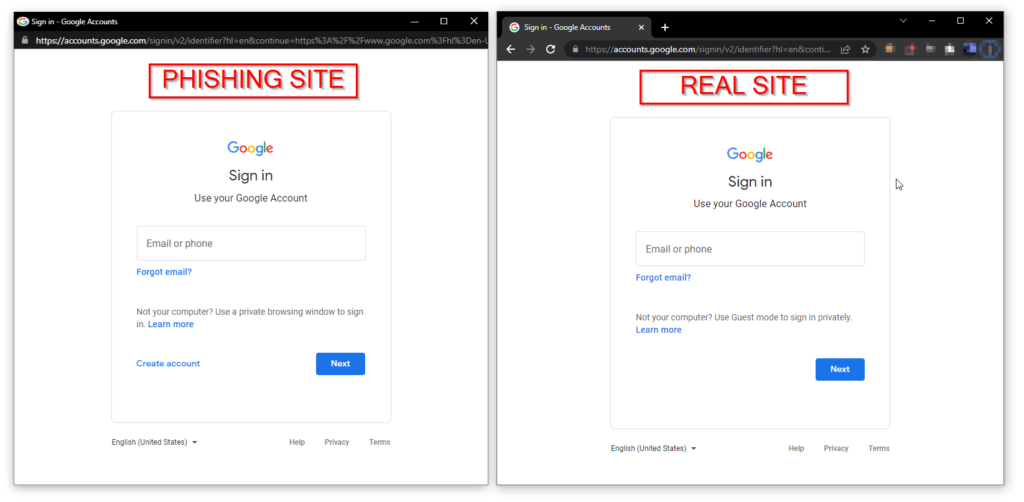
They could choose an attractive address and content that may lure victims — such as shopping deals, job opportunities, or news a user might want to comment on. The criminals set things up so that visitors need to sign in if they want to buy something, comment, or access other features that interest them. Then the malefactors add buttons that supposedly permit logging in through the legitimate services they want to harvest passwords from. If victims click on such a button, they’ll see a login window they’re familiar with, such as a Microsoft, Google, or Apple prompt, with the correct address, logo, and input fields — in short, all the components of the interface they’re used to seeing. The window can even display correct addresses when users hover the mouse over the “Log in” button and “Forgot password” link. The catch is that this isn’t actually a separate window — this marvel of deception is scripted to appear right on the page that is trying to trick the user. If you enter your credentials in this window, they won’t go to Microsoft, Google, or Apple, but rather straight to the cybercriminal’s server.
Phishing is when attackers send malicious emails designed to trick people into falling for a scam.
Scammers create fake profiles on legitimate dating websites and try to enter into a relationship with you so they can get a hold of your money and personal details
Scammers send emails, text messages or make a call that appear to be from your bank, a financial institution or an online payment service
An attack is a novel phishing technique that replicates pop-up windows used for SSO in an effort to steal login credentials. It works like this[:] The cybercriminals register a website using the classic phishing technique of making a clone of a legitimate website
References on how to protect yourself from scamming: